Use SM2/SM3 in Hyperledger Fabric 1.4
To understand why we want to change the default encryption method, we need to have a basic understanding of openssl, gmssl & bccsp.
Background
OPENSSL
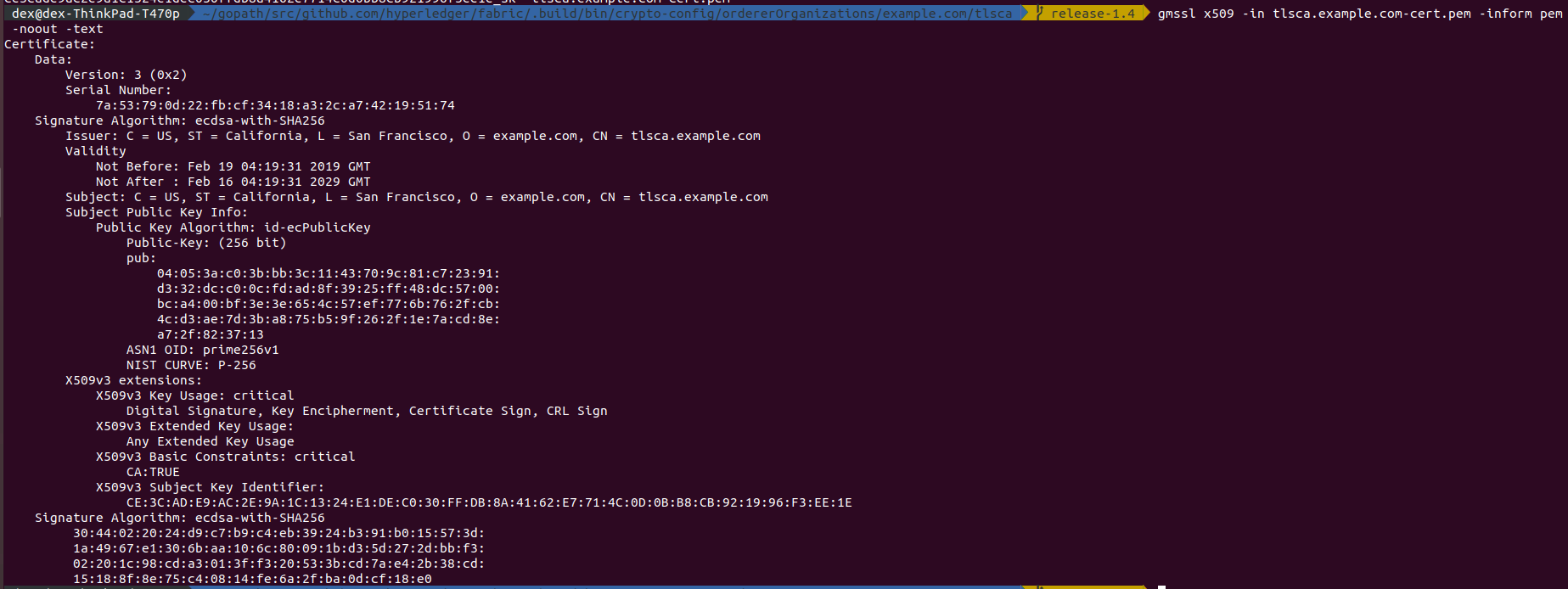
How to check the certificate
openssl x509 -in <> -inform pem -noout -text
Lexicons in OPENSSL
.csr(Certificate Signing Request) - a block of encoded text that is given to a Certificate Authority when applying for an SSL Certificate.der.key.p12.pfx
GMSSL
How to check the certificate
gmssl x509 -in <> -inform pem -noout -text
BCCSP
The interface of bccsp can be found there
type BCCSP interface {
// KeyGen generates a key using opts.
KeyGen(opts KeyGenOpts) (k Key, err error)
// KeyDeriv derives a key from k using opts.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the primitive used.
KeyDeriv(k Key, opts KeyDerivOpts) (dk Key, err error)
// KeyImport imports a key from its raw representation using opts.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the primitive used.
KeyImport(raw interface{}, opts KeyImportOpts) (k Key, err error)
// GetKey returns the key this CSP associates to
// the Subject Key Identifier ski.
GetKey(ski []byte) (k Key, err error)
// Hash hashes messages msg using options opts.
// If opts is nil, the default hash function will be used.
Hash(msg []byte, opts HashOpts) (hash []byte, err error)
// GetHash returns and instance of hash.Hash using options opts.
// If opts is nil, the default hash function will be returned.
GetHash(opts HashOpts) (h hash.Hash, err error)
// Sign signs digest using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
//
// Note that when a signature of a hash of a larger message is needed,
// the caller is responsible for hashing the larger message and passing
// the hash (as digest).
Sign(k Key, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (signature []byte, err error)
// Verify verifies signature against key k and digest
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Verify(k Key, signature, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (valid bool, err error)
// Encrypt encrypts plaintext using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Encrypt(k Key, plaintext []byte, opts EncrypterOpts) (ciphertext []byte, err error)
// Decrypt decrypts ciphertext using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Decrypt(k Key, ciphertext []byte, opts DecrypterOpts) (plaintext []byte, err error)
}
Lexicon for BCCSP
ski: subject key identifiercsp: cryptographic service providerhsm: Hardware security module - a physical computing device that safeguards and manages digital keys for strong authentication and provides crypto processing1X.509- a standard defining the format of public key certificates2 (This is also used in MSP/Membership Service Provider)public key certificate/digital certificate/identity certificate- an electronic document used to provde the ownership of a public key3public key cryptography4 - a cryptographic system that uses pairs of keys: public keys which may be disseminated widely, and private keys which are known only to the owner5.PKI: Public-key infrastructureecdsa: Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm -
Steps to add sm2/sm3 support for Fabric
- Clone the Hyperledger/fabric under
GOPATH
For example,
mkdir -p ~/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
cd ~/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
# OPTIONAL, if not exist
git init
git remote add origin git@github.com:hyperledger/fabric.git
git fetch --all
git checkout release-1.4.0
# END OPTIONAL

- apply the patch
git clone git@github.com:flyinox/fabric-sm-patch.git
git am fabric-sm-patch/fabric-sm-patch
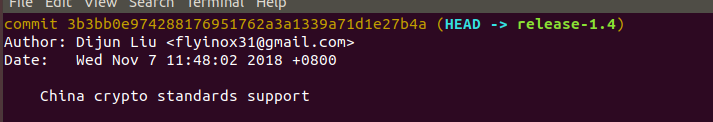
Make sure the HEAD is correct,
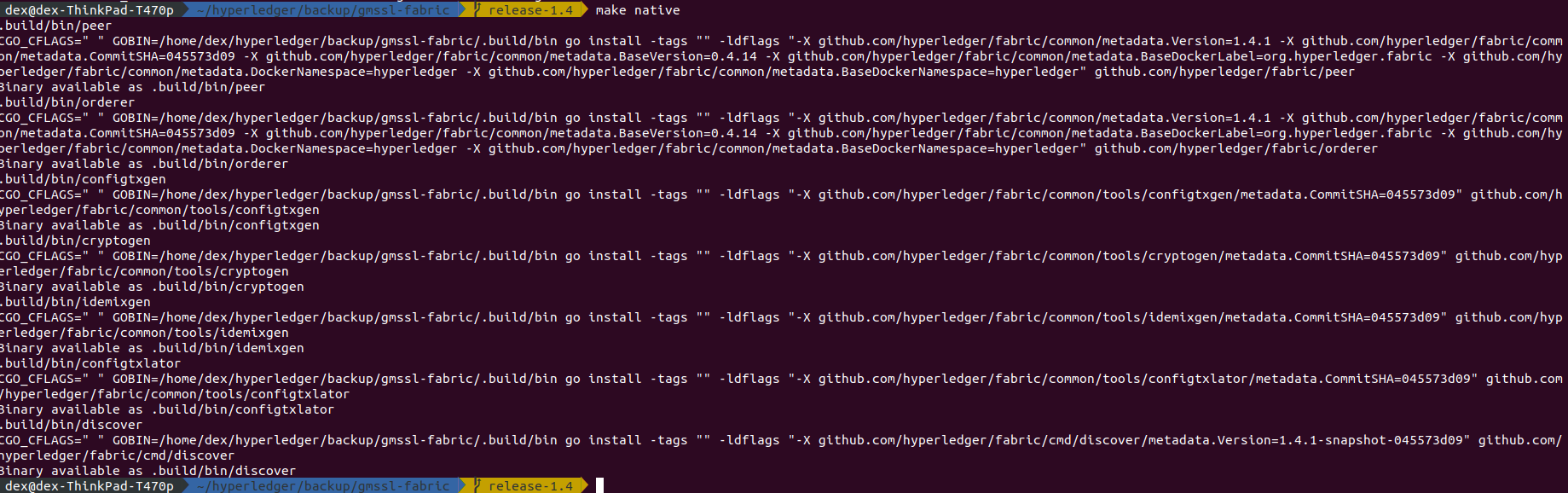
- compile to executable
Note: You can also check the target compiling file by go list -f '' under common/tools/cryptogen

But you can also build the file directly by,
# under <FABRIC>/common/tools/cryptogen
go build mainsm.go
make native
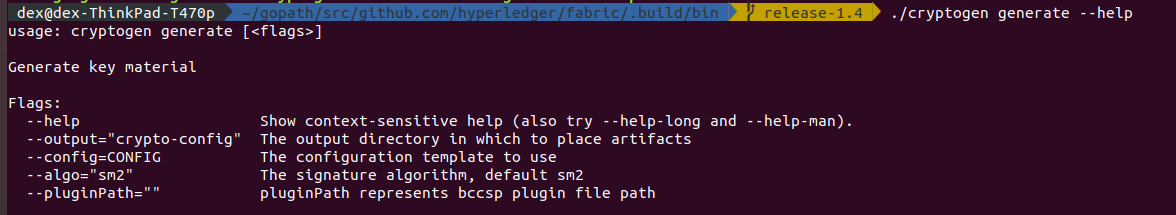
- generate crypto-config
# USE cryptogen to generate certificates with sm2/sm3 signature
.build/bin/cryptogen generate --help
You should see the following message,
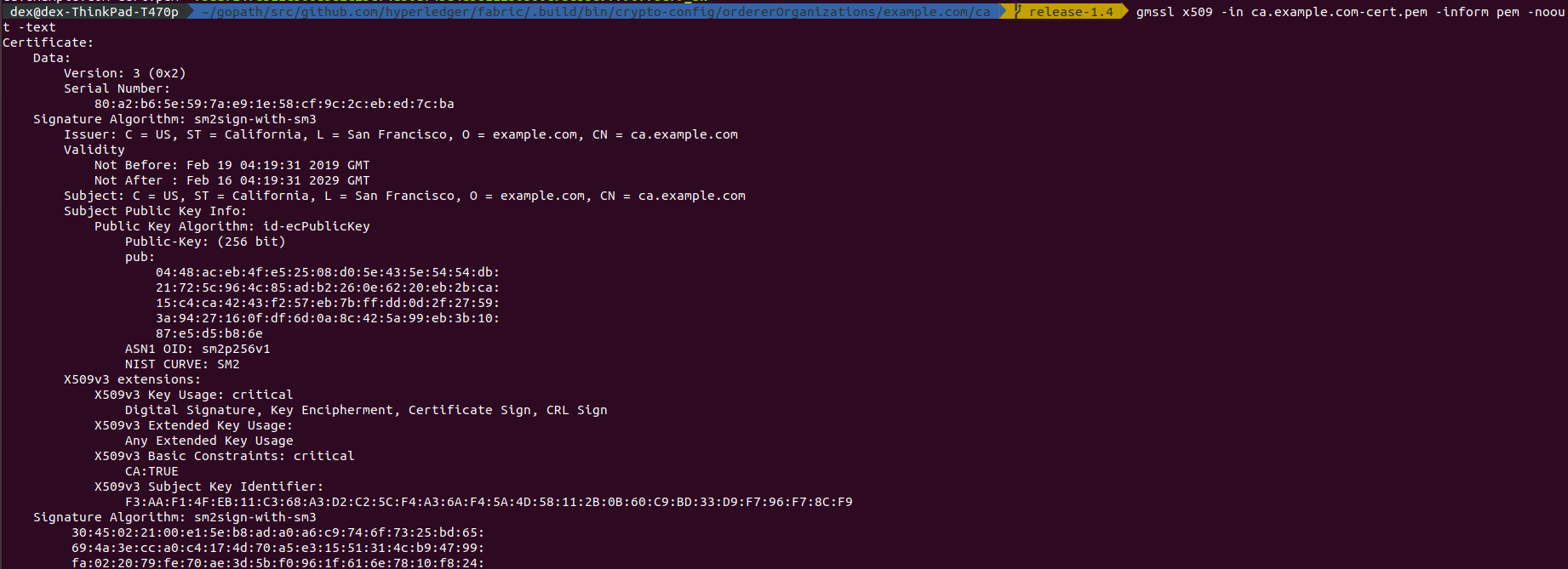
An example certificate for orderer,
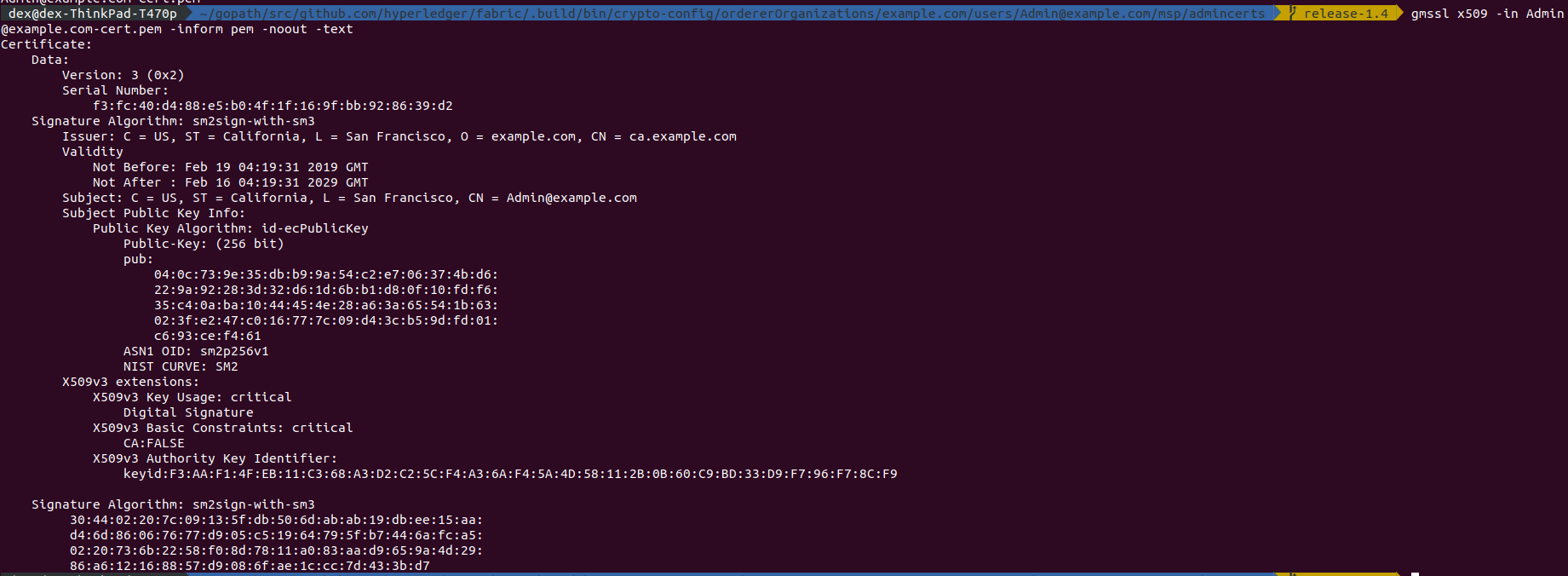
Or Admin,
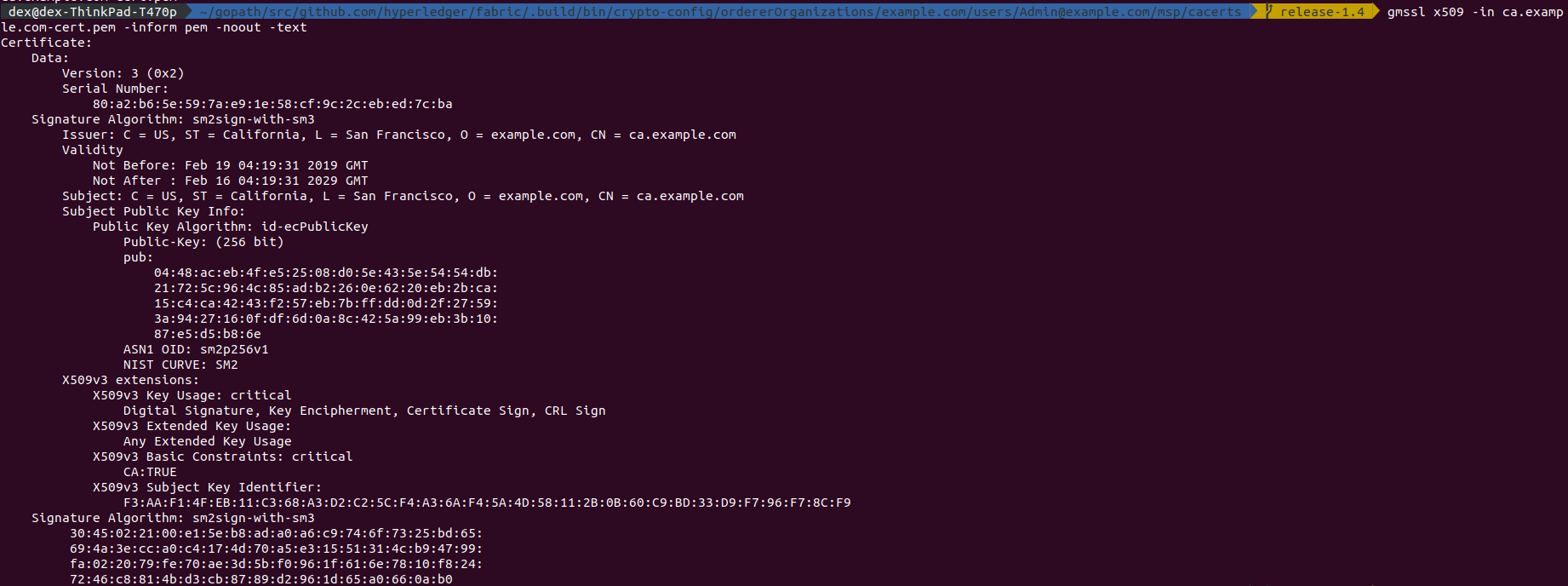
Or MSP CA,
However, for tlsca the signature algorithm is NOT modified,